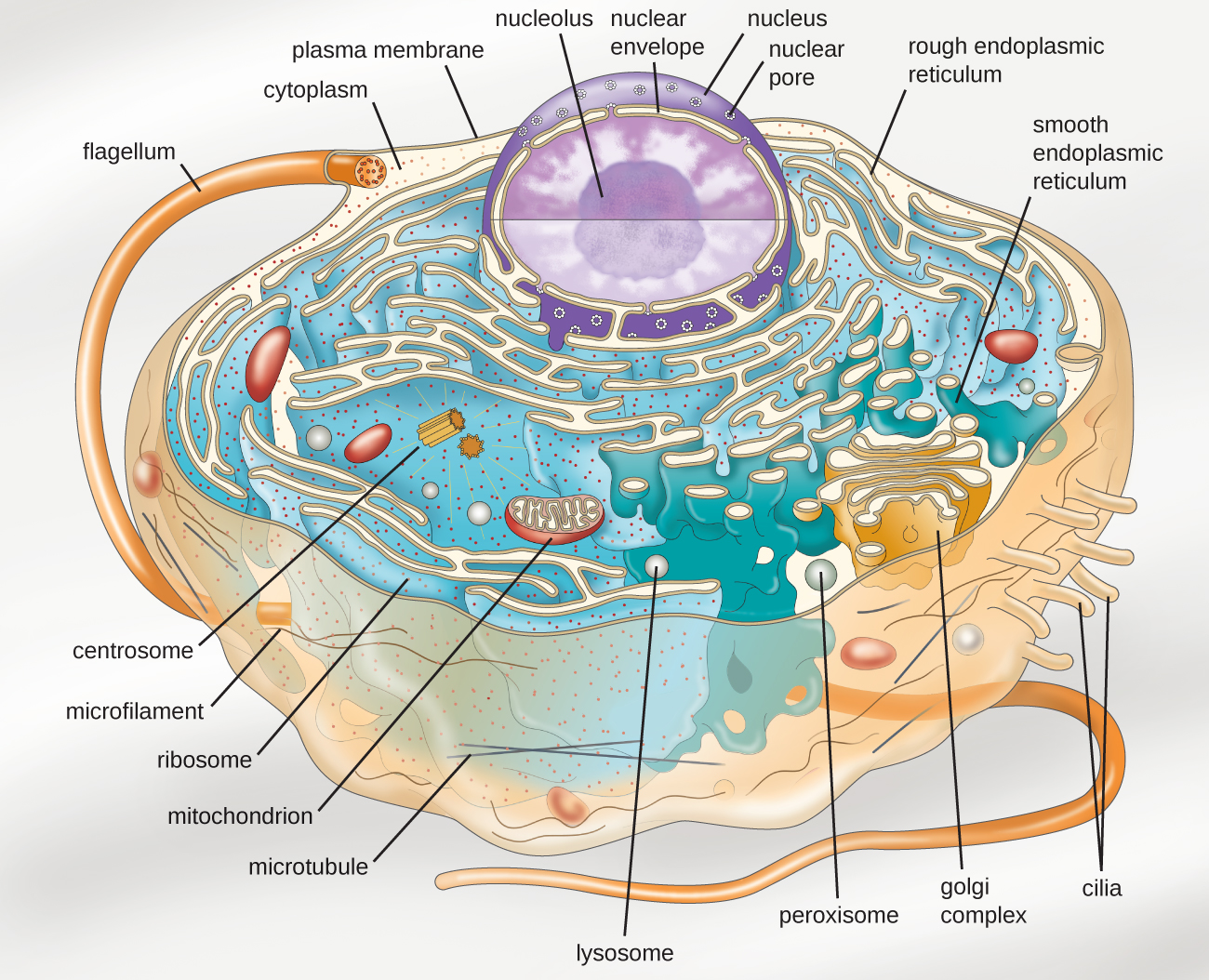
3.4 Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology 201
Eukaryotic cells are much more complicated than those of prokaryotes. They are packed with a fascinating array of subcellular structures that play important roles in energy balance, metabolism, and gene expression.
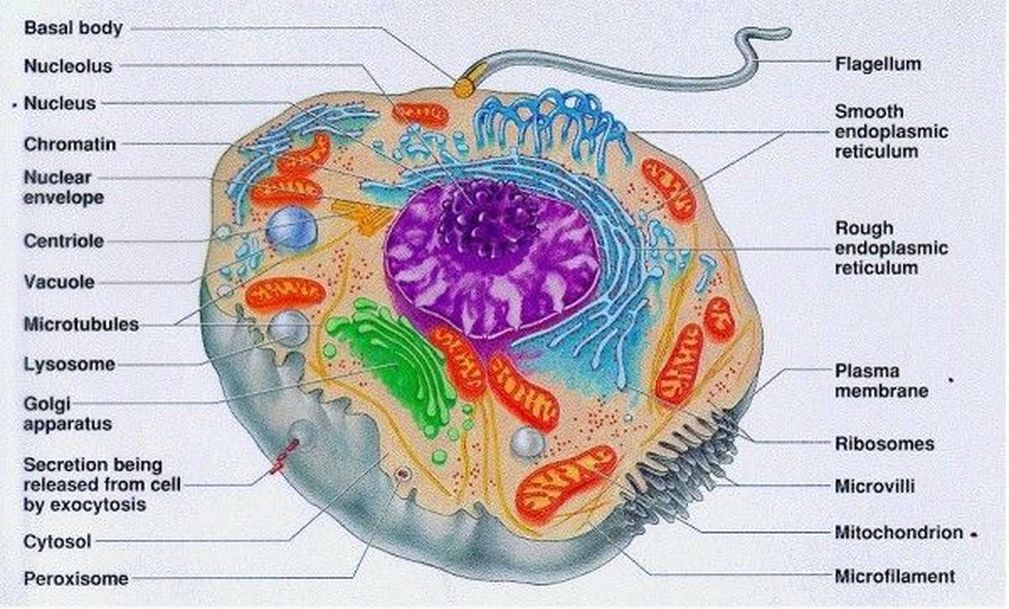
2.4 Eukaryotic Cell Structure a level biology student
Stephanie Castle 23.3K subscribers Subscribe Subscribed 26K views 8 years ago Topic 1: Cell Biology (Old Syllabus Last Exams 2024) Drawing eukaryotic cells and annotating the functions of.

Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cellular Structures ALevel Biology Revision Notes
Definition A eukaryotic cell contains membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and an endoplasmic reticulum. Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. These organisms are grouped into the biological domain Eukaryota.
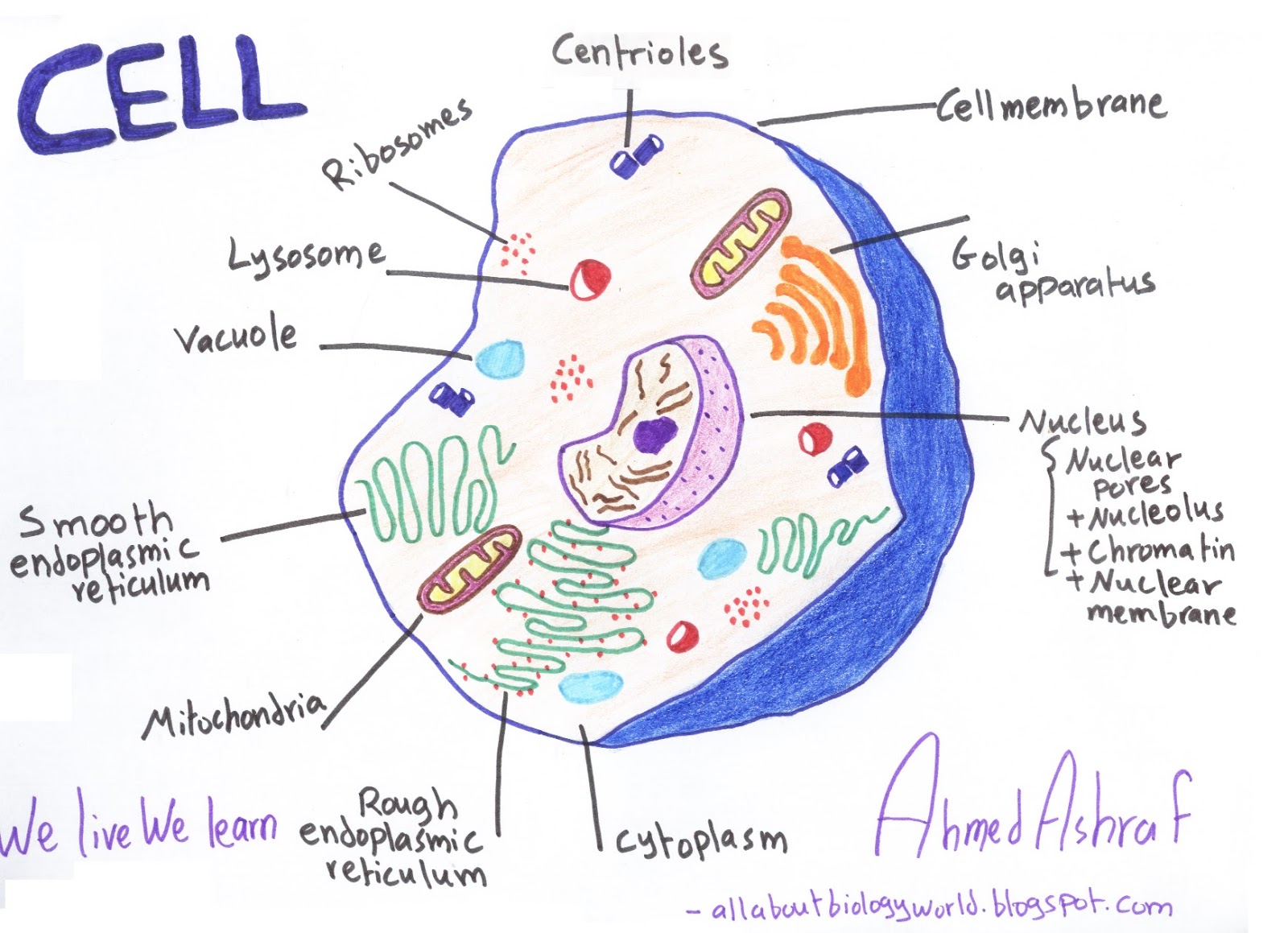
Biology Club Our cells 1 ( structure, function, division, disorder & cycle )
How to draw Eukaryotic cell/ step by step drawing for beginners eukaryotic cell, eukaryotic cell diagram, step by step drawing for beginners, biology diagram, diagrams, how to draw.
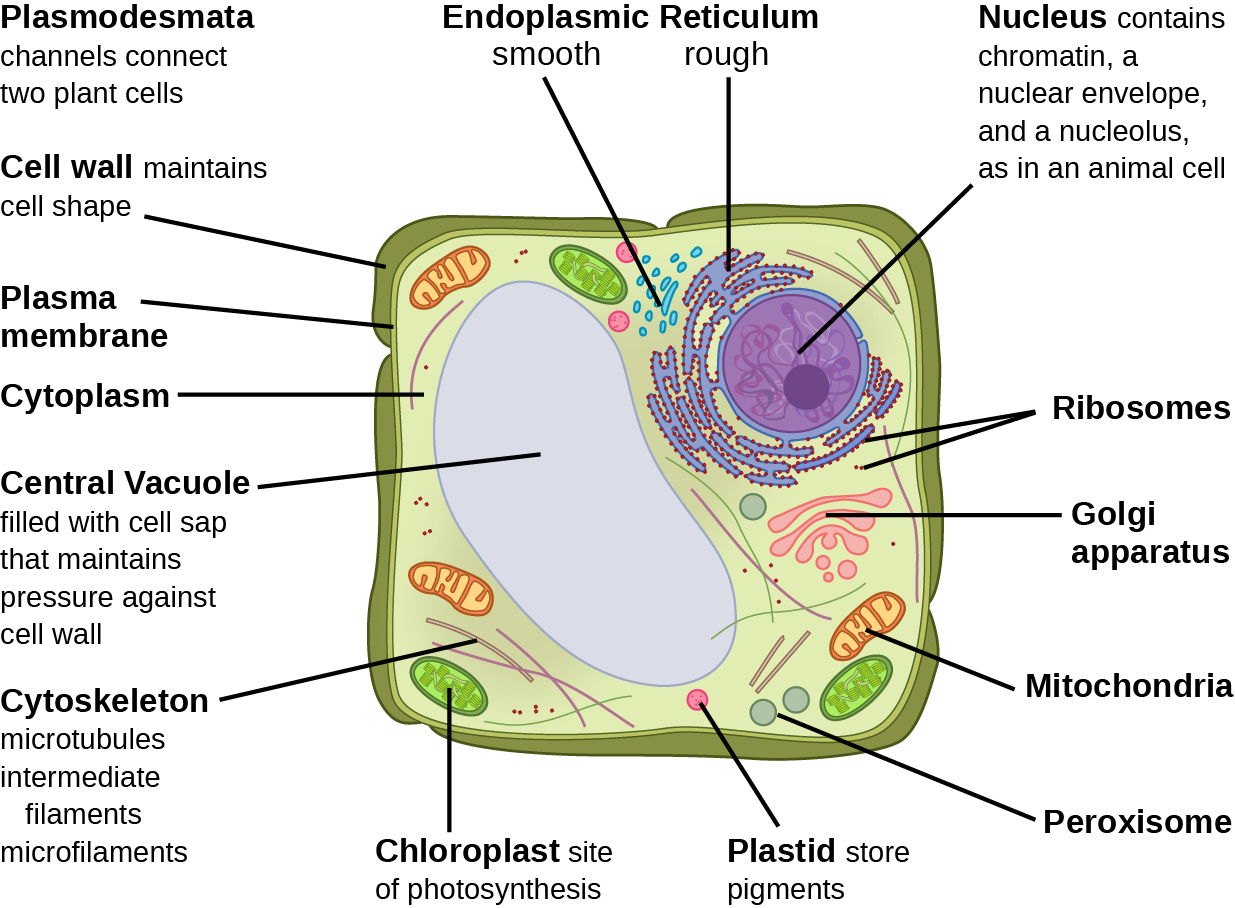
Biology 2e, The Cell, Cell Structure, Eukaryotic Cells OpenEd CUNY
Key points: Gene regulation is the process of controlling which genes in a cell's DNA are expressed (used to make a functional product such as a protein). Different cells in a multicellular organism may express very different sets of genes, even though they contain the same DNA.

Diagram Of A Eukaryotic Cell Drivenheisenberg
Eukaryotic cells typically have their DNA organized into multiple linear chromosomes. The DNA within the nucleus is highly organized and condensed to fit inside the nucleus, which is accomplished by wrapping the DNA around proteins called histones. Figure 5.1.3 5.1. 3: Eukaryotic cells have a well-defined nucleus.

Parts and functions of eukaryotic cell
A eukaryotic cell is an advanced type of cell that has a well-defined nucleus and multiple membrane-bound organelles. DNA is the genetic material of the eukaryotic cell. The nucleus is surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane. Eukaryotic cells have mitochondria for cellular respiration.

Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Characteristics, Structure and Examples
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright.

Parts of the Eukaryotic Cell Diagram Quizlet
MCAT > Foundation 2: Cells > Eukaryotic cells Cellular organelles and structure Google Classroom What is a cell Right now your body is doing a million things at once. It's sending electrical impulses, pumping blood, filtering urine, digesting food, making protein, storing fat, and that's just the stuff you're not thinking about!
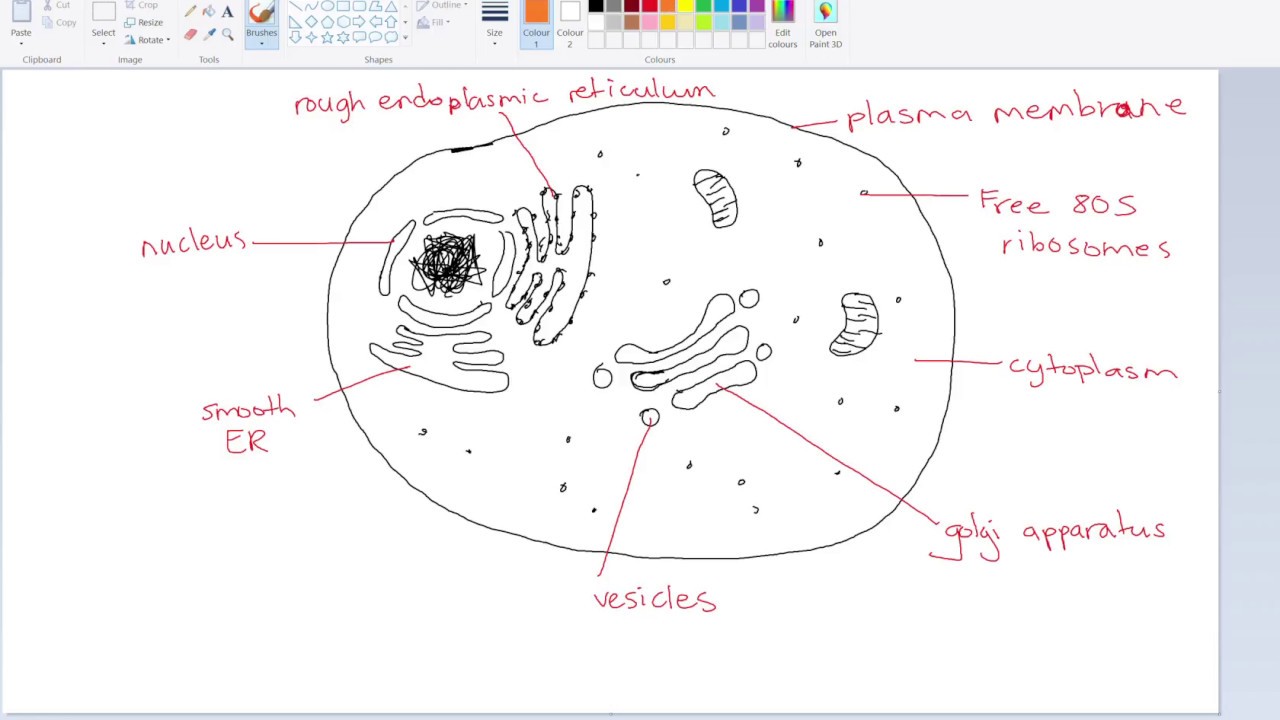
How to draw a Eukaryotic Cell IB Biology YouTube
Phases of the Cell Cycle. A typical eukaryotic cell cycle is illustrated by human cells in culture, which divide approximately every 24 hours. As viewed in the microscope, the cell cycle is divided into two basic parts: mitosis and interphase.Mitosis (nuclear division) is the most dramatic stage of the cell cycle, corresponding to the separation of daughter chromosomes and usually ending with.

1.4. Eucaryotic cell structure Biolulia European Sections
Introduction to eukaryotic cells. By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells are characterized by numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others.
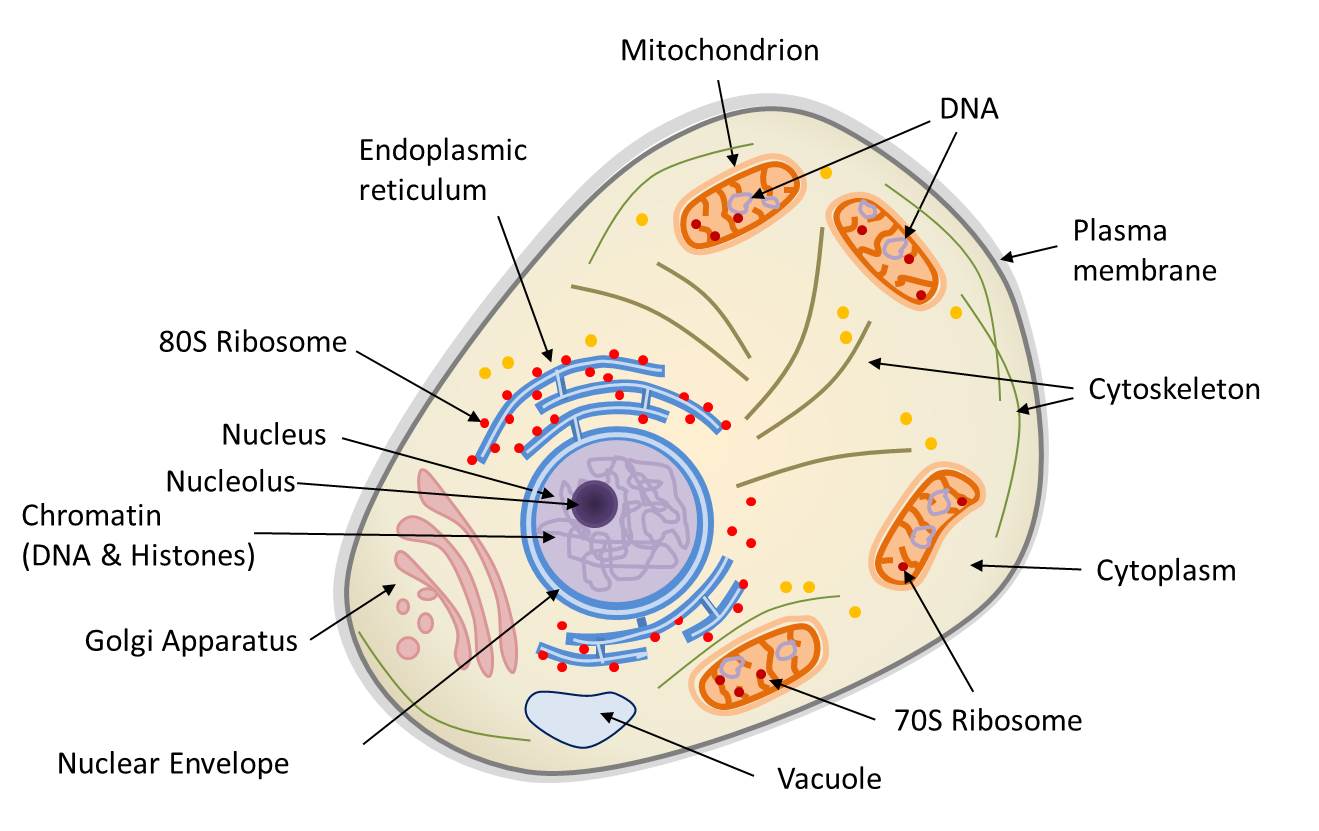
Symbiosis and evolution at the origin of the eukaryotic cell Encyclopedia of the Environment
Eukaryotic cells are characterized by a membrane-bound nucleus. That's distinct from prokaryotic cells, which have a nucleoid - a region that's dense with cellular DNA - but don't actually have a separate membrane-bound compartment like the nucleus. Eukaryotic cells also have organelles, which are membrane-bound structures found within the cell.

Biology 101 Cells Owlcation
Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: 1) a membrane-bound nucleus; 2) numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; and 3) several, rod-shaped chromosomes. Because a membrane surrounds eukaryotic cell's nucleus, it has a "true nucleus."
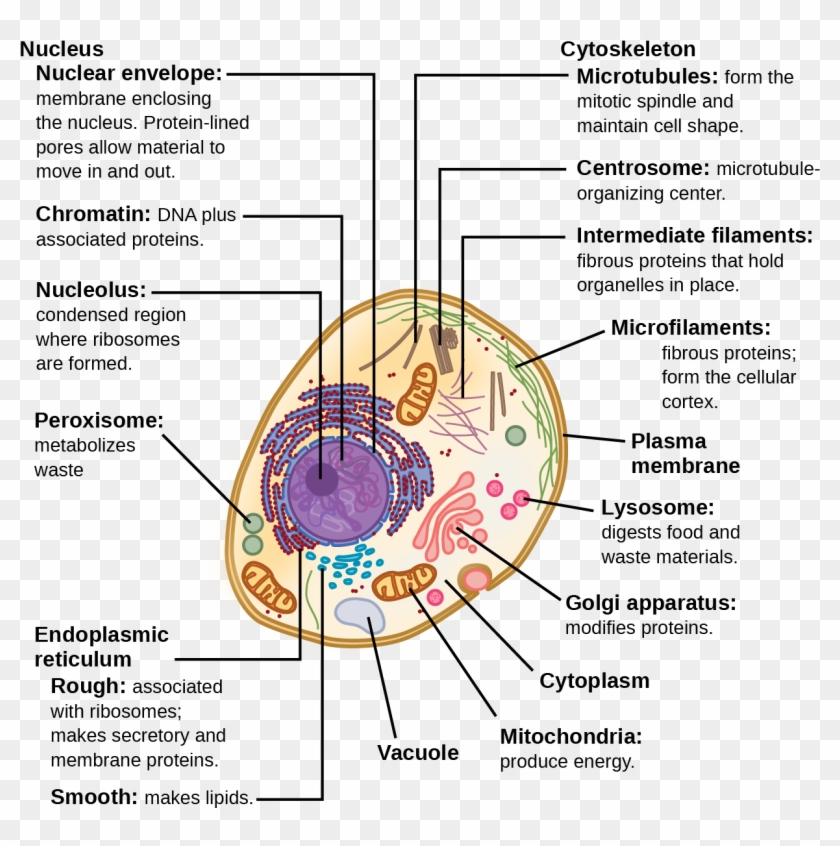
Chromatin Drawing Eukaryotic Cell Structure Of A Typical Eukaryotic Cell, HD Png Download
Like prokaryotes, eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane (Figure 2) made up of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates the internal contents of the cell from its surrounding environment. A phospholipid is a lipid molecule composed of two fatty acid chains and a phosphate group. The plasma membrane regulates the passage of.
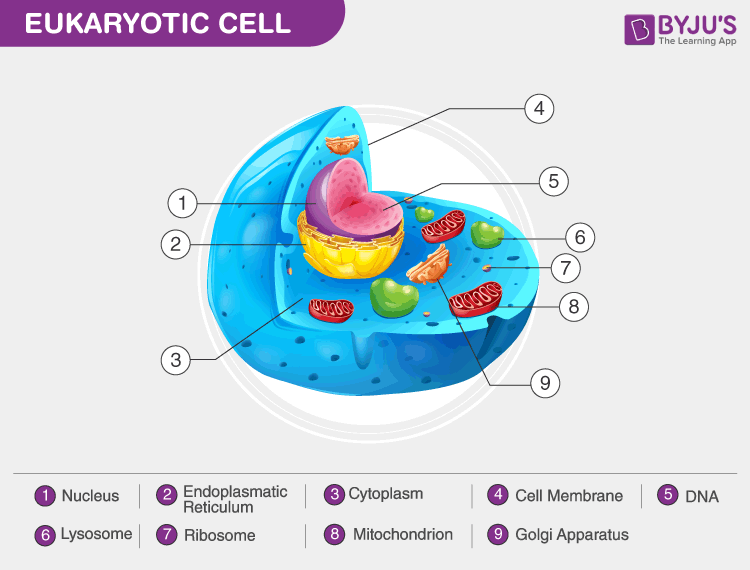
Eukaryotic Cells Definition, Characteristics, Structure, & Examples
Eukaryotic cells 2.3.1 Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell.. Figure 2.3.1 - Annotated drawing of an animal cell. 2.3.2 Annotate the diagram from 2.3.1 with the functions of each named structure.. Ribosomes: Found either floating free in the cytoplasm or attached to the surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum and in mitochondria and.

Animal eukaryotic cell structure
Explanation Characteristics Structure Diagram Cell Cycle Examples What is a Eukaryotic Cell? Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane and form large and complex organisms. Protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. They are classified under the kingdom Eukaryota.